INTRODUCTION
Obesity" specifically refers to an excessive amount of body fat. Obesity is defined as an excessively high amount of body fat or adipose tissue in relation to lean body mass. The amount of body fat (or adiposity) includes concern for both the distribution of fat throughout the body and the size of the adipose tissue deposits. Body fat distribution can be estimated by skin fold measures, waist-to-hip circumference ratios, or techniques

YOGA AND OBESITY
Yoga has an important role to play in the treatment of Obesity. Yoga techniques affect body, internal organs, endocrine glands, brain, mind and other factors concerning Body - Mind complex. Various Yoga techniques can be practiced effectively to reduce the weight and achieve normal healthy condition of Body and Mind. Yoga positions or postures are especially useful to reduce the fats in various parts, especially forward bending, twisting and backward bending asanas help reduce the fats near abdomen, hips and other areas.

YOGA POSES FOR OBESITY
Gate Pose
Gate pose, also known as ptarmigans stretches the side of the body and is very useful for toning the abdominals, improving circulation and increasing the flexibility of the spine. This pose stretches the muscles connecting to ribs, thereby increasing the capacity of the lungs for deep breathing. Stretches the sides of the body and makes the spine flexible. Tones the abdomen and improves circulation helping in obesity.
Seated Forward Bend Pose
Relax your body and mind, stretch your hamstrings, shoulders, and spine, relieve stress, and improve your posture and concentration by practicing the Seated Forward Bend
Cows Face Pose
Gomukha literally means "cow face" in Sanskit.Place both feet on the ground with heels crossed under the buttocks. Sit straight and still, the mouth raised. This is called Gomukha-asana, resembling the mouth of a cow. This posture stretches the arms, upper back, chest and the sides of the chest and abdomen. As the shoulder blades are stretched backward the lungs are expanded and as the abdominal muscles are lifted the stomach is toned.
Boat Pose
Perform the Boat Pose to strengthen your abdominal area and hip flexor, tone muscles in the midsection, improve digestion, and relieve stress. You can use a Yoga Strap to aid you in holding the pose longer or if you cannot keep your legs straight.
The Eagle Pose
The Sanskrit word garuda means eagle. In Hindu mythology Garuda is known as the king of birds. This pose will strengthen the legs, knees and ankles. It stretches and tones muscles of the leg and can help relieve cramps of the legs and also helps in treating obese condition.
Mountain Pose
The Mountain Yoga Pose promotes the experience of stillness, strength, relaxed power, and immovable stability associated with mountains. This yoga posture, and coming back to this stillness after other poses, is one of the ways of becoming acquainted with stillness.
Warrior Pose One
The Warrior Pose I or Virabhadrasana I improves balance and agility and strengthen your legs, back, and arms. It also targets the chest, shoulders, neck, and abdominal area.
Corpse Pose
This pose, the final stage in a yoga session, relaxes and refreshes the body and mind. To come into this posture, lie on your back, arms by your sides, your palms facing up. Breathe deeply and slowly through the nostrils until the pose is completed. Your legs should be straight and together, with your feet rolled out to the sides. Tilt your forehead slightly higher than your chin. Let your body completely relax. Clear your mind of all stress, tension, and worries. Hold the pose for 10 minutes and then release.
YOGA ASANAS FOR OBESITY
SUNSALUTATIONS

Sun salutations are very beneficial in Obesity management, every day 24 sun salutations with a speed of 4 rounds in 1 minute gives great benefits of Yoga Asanas and exercise as well.
The practice of Sun salutation is a sequence of 7 asanas practiced in order which tones almost all of the muscles and also internal organs are stretched increasing blood & oxygen supply to these parts ;
Regular practice of sun salutation with breathing gives good exercise to the lungs. Mantras have relaxing effect on mind.
PRANAYAMAA

Pranayama is very important technique in yoga which is control and extension of Prana or Vital energy or Life force. Pranayama helps in management of this energy. Various techniques are available in yoga, which give interesting but good results. The Pranayama can be classified in 2 types in terms of physiology, Hypo ventilation or vitalizing Pranayama and Hyper ventilation or relaxing pranayama. Kapalbhati, Bhasrika and Fast breathing can be classified under Hyper ventilation (increases Oxygen and reduces carbon dioxide) and Deep breathing, Bhramari, Shitali, Sitkari can be classified as Hypo ventilation (oxygen level remains mostly same but the speed of respiration is lower, heart rate lower).Kapalbhati, Bhasrika & fast breathing can be practiced by people suffering from obesity with good effects; these Pranayama techniques increase the lung capacity and help burning fats. Regular practice of Pranayama brings balance in the system in terms of Physical and Mental functions.
TRIKONASANA
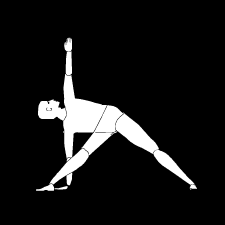
Trikonasana is one of the most important Yoga postures. Trikonasana stretches the spine, opens the trunk and improves balance and concentration. Rotate your left foot for about 90 degrees to the left and your right foot about 45 degrees inward.Trikonasana is considered therapeutic for anxiety, flat feet, infertility, neck pain, osteoporosis, and sciatica. The regular practice of yoga is health promoting, and this pose may be helpful to individuals with those conditions.
Steps
• Sit with your legs fully stretched out. Bend each leg at the knees and place your feet on the other hip joint. Both the heels are adjusted in such a way that each presses the adjacent portion of the abdomen. This forms the foot-lock in a sitting position.
• Bend backwards and, exhaling, rest your weight on the elbows. Push your neck backwards and slightly rise the hip upward thus making an arch of the spine.
• Then, by making hooks of the forefingers, hold your toes on the corresponding side without crossing your arms.This posture should be maintained for some time with slow and deep breathing.
• For reverting to the original position, release the foot-lock and return to the supine position by lowering the arch.
BHUJANGASANA
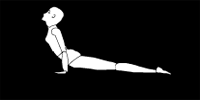
This asana is concerned with the spinal cord and the muscles of the stomach and helps in obesity. Due to the stretching the efficiency of the digestive organs increases. To some extent back problems are reduced as the blood circulation is improved.
Steps
• Bring both the hands close near chest and place palms on the ground. Touch the forehead on the ground.
• Inhaling first raise the forehead and chin bend neck as much as possible and start raising the shoulders at ease giving pressure to each Vertebra of the backbone.
• Raise the chest along with till the hands become straight.
• Take the neck back, start normal breathing.
• In the final position keep the hands straight, chest forward. Keep the spine in arch.
• Inhale and exhaling, with the support of the spinal column, start lowering the shoulders slowly with first abdomen touching the floor and then chest, forehead.
• Place the chin on floor and hands back to the original position. Attain prone position.
VEERASANA
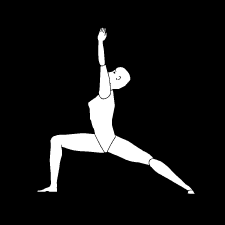
Vira means brave. The way a brave man takes position while attacking his enemy, the similar position is formed in this asana, hence it is called as Virasana.In this asana the joints of the legs, the waist, the spinal column and the neck get curved in opposite direction. As a result of this, the blood circulation to these joints is regulated. The spinal column becomes elastic and its functioning improves. There is pressure on the digestive organs and the belly gets stretched, which promotes their functioning.
Steps
• Take the left foot forward and place the left foot on the floor at the maximum distance from the initial position.
• Bring both the hands together, join the palms and place them on the knees of the left leg. Bend the left leg in the knee in such a way that the thigh and the calf come in 90 degrees. Keep the right leg straight.
• Raise the joined hands up and take them back above the head and then without bending the hands in the elbows, bend the head backward and keep the sight backward down.
• The front leg should be bent in 90 degrees angle and the back leg should be straight. Keep the toes frontward.
• The back leg, the back, the neck and both the hands form a very good arch in this position and this forming of arch is desirable, too.
• The body should be weighed backward and keeping the arms near the ears, the neck should also be bent downwards.
• Start bringing the body forward and place the hands on the knee. Keep sight to the front.
• Straighten the knee and restore the hands to their original place.
• Restore the left leg to its place and take up standing position.
PASCHIMOTTANASANA
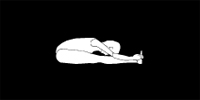
Paschimottanasana is a fine stretching exercise of the body. In one continuous movement, almost all the posterior muscles get fully stretched and relaxed. This helps to improve the functions of the abdominal organs and sets right respiratory disorders. It also helps to improve memory.
Steps
• This posture involves stretching of the posterior muscles of the body.
• While sitting, stretch your legs forward and keep them close to each other. Bend a little forward, make hooks of your fingers and hold the big toes on the respective sides.
• While exhaling, bend forward stretching the trunk along the thighs. Rest your on the knees, which should be kept straight.
• Gradually, the tense muscles can be made supple for securing the complete posture. Inhale and return to the original position
HALASANA

This asana improves digestion and strengthens the spine. It helps in asthma, diabetes, menstrual disorder and constipation. It helps in conditions like obesity.
Steps
• Lie flat on your back with legs and feet together, arms at the sides, closed and placed beside the thighs.
• Keeping your legs straight, inhale slowly, and raise your legs to 30, 60 and 90, pausing at each stage. While exhaling push your legs further over and above the head and then beyond, so that they touch the floor (without bending the knees).
• Stretch your legs as far as possible so that your chin presses tightly against the chest. Then raise your hands and try to hold the toes. Retain the pose from 10 seconds to three minutes. Breathe normally.
• While exhaling, return to the standing position. Slowly go through the process in the reverse order.
DHANURASANA
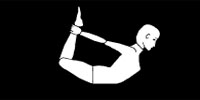
This asana strengthens the abdomen, especially around the navel, and the chest muscles. It improves the flexibility of the arms, shoulders, thighs, legs, lower back and abdomen. The spine also becomes healthy and strong. It is good for relieving flatulence, constipation and menstrual irregularities. It also prevents sterility.
Steps
• Lie down with face and the forehead touching the ground, arms extended along side the body and legs straight.
• Bend your legs at the knees towards the hips, bringing them forward so that they can be held firmly by the hands at the ankles on the respective sides.
• While inhaling, stretch your legs backwards and raise your thighs, chest and head simultaneously. Hands should be kept straight. The weight of the body should be on the navel. Knees should be kept close, if possible, with eyes looking upwards. This posture should be retained for at least a few seconds, holding the breath.
ASTROLOGY
Yoga has been an ancient practice perfected for centuries. Even though modern science has found its own set of cures for the body, yoga remains a natural way to deal with the day-to-day problems we face. Mastering this art will take time but it's never too late to start to make it an integral, positive part of your daily life. According to astrological reports for yoga asanas the above mentioned asanas are said to be effective for those who come under the following zodiac sign.
• TAURUS
• AQUARIUS